
TVB is ideal for dealing with bursty workloads - programs that cause a sudden spike in CPU utilization. A high-performance air or liquid cooler, such as a Cryo Cooler, will help your system stay below the threshold. It’s another building block in the stack of technologies that allow 11th Gen Intel® Core™ CPUs to reach higher Max Turbo Frequencies.įor 11th Gen Intel® Core™ desktop CPUs, TVB increases clock frequency by 100 MHz when the processor is below a temperature threshold of 70☌. Introduced in 2018, Intel® Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB) is a technology that unlocks extra CPU performance when thermal headroom and turbo power budget are available. It’s included in both 11th Gen Intel® Core™ i9 and i7 CPUs, such as the Intel® Core™ i7-11700, which features a max turbo frequency of up to 4.9 GHz.Īs with other boost technologies, your CPU must be running below power, current, and temperature specifications for Intel® Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 to take effect. Games and many common applications rely 4 on high-frequency cores and benefit from Intel® Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0. Other 11th Gen boost technologies provide all-core boosts that benefit highly parallelized programs. Multi-threaded applications, by comparison, perform more work in parallel, scaling with more cores and features like hyper-threading. This helps benefit performance in lightly-threaded applications. It’s another technology that provides an extra boost to the favored core(s). Intel® Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 doesn’t replace Turbo Boost 2.0. Intel® Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 identifies up to two of the fastest cores on your CPU, known as “favored cores.” Then it applies a frequency boost to those cores (or that core) and directs critical workloads to them. Works below a temperature limit of 100☌.ĭue to production differences, processor cores vary in maximum potential frequency. Opportunistically increases all-core turbo frequency when current, power, and thermal headroom exists. Ultra fast speeds when all cores are active and the CPU is under its temperature threshold. Takes the faster of the two favored CPU cores to a speed superior to Turbo Boost Max 3.0. Intel® Core™ i9 desktop CPUs (except i9-11900T) Opportunistically increases clock frequency by up to 100MHz available if the CPU’s within temperature limits (70☌ for desktops, 65☌ for mobile) and turbo power budget is available.

Intel Core i7 and i9 desktop CPUs Intel® Core™ i9 and i7-11375H mobile CPUs (Before overclocking.) If the system has sufficient power and thermal headroom - think a high-performance air or liquid CPU cooler - it can make this leap in frequency to better handle more intensive workloads.īoosts all-core frequency above base clock speed up to specified maximum frequency during more intensive workloads available if the CPU’s running under its power, current, and temperature limits.īoosts the frequency of one or two favored cores available if the CPU’s running below its power, current, and temperature limits. But its max turbo frequency is much faster: 5.3 GHz. It’s the maximum single-core frequency a CPU achieves without overclocking.įor example, the Intel® Core™ i9-11900K has a base frequency of 3.5 GHz, meaning it completes 3.5 billion cycles per second.
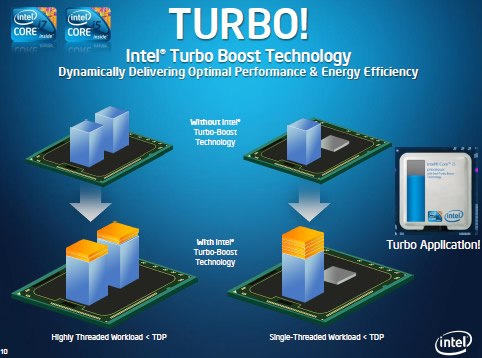
Max turbo frequency is the frequency a CPU targets when stressed by a demanding application like a game.
#Intel turbo boost technology monitor 3.0 for i5 full
Operating at a lower frequency some of the time - as opposed to full speed all of the time - can also aid processor longevity 4. When running at its base frequency, the CPU draws less power and produces less heat. They do this by increasing the CPU’s frequency, or clock speed.īefore we discuss how boosting behaviors work, there are two specifications to understand.īase frequency is the frequency at which the CPU runs when the system is idle or under light load. But heavyweight tasks like gaming, editing video, or streaming content are more taxing.īoost technologies address this difference and help Intel processors adapt to the job at hand. Typically, processors can easily handle lightweight requests like running a word processor or browsing the web. Different workloads place different demands on a system’s CPU.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
